
1.2 Heat exchangers of «annular tubes» type
Heat exchangers of "annular tubes" type is used mainly for cooling or heating in a «liquid-liquid» system, when the coolant flow rate low and the latter do not change their state of aggregation. Sometimes such heat exchangers are used in high pressure for liquid or gaseous medias, such as condensers in the production of methanol, ammonia, etc. They are also used for the contaminated of coke-forming substances and mechanical impurities of the coolants, which ensures good heat transfer due to high velocities and turbulence in the flow tubes and the annulus. The high speed and turbulence reduce the possibility of deposition of coke on the walls of the tubes or other structures.
Heat exchangers of this type consist of a number of series-connected units (Figure 1.22).
Each unit consists of two coaxial tubes. To achieve ease of cleaning and replacement, inner tubes are usually interconnected by the «kalatches» or tribes. Compared to the shell and tube heat exchanger, heat exchangers of "annular tubes" type has a lower flow resistance of the annulus. However, under the same heat exchange characteristics they are less compact and more metal than shell and tube heat exchanger. Heat exchanger of «annular tubes» can be collapsible or hardwired, single and multi-stream
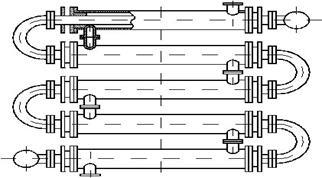
Figure 1.22 – Heat exchangers of «annular tubes» type
A single-threaded molded heat exchanger (Figure 1.22) consists of separate units, each of which consists of the outer tube (or shell tube) and internal (or heat exchanger). The outer tube with two welded rings connected with the inner tube in the unit. Units, in turn are assembled in a vertical row and constitute a heat exchange section. This inner tubes interconnected by the tribes and outdoor by the fittings on the flanges. The units are fixed on a metal frame brackets.
Molded heat exchangers have a construction of rigid type, so when the temperature difference of more than 70 °C, they are not used. In larger temperature difference of the tubes, and if necessary, mechanical treatment of the annulus usually are used exchangers with the compensating mechanism on the outer tube. In this case, the annular gap between the tubes with one hand tightly brew, but on the other - seal by the gland. Direction of flow in the heat exchanger of "annular tubes" type is shown in Figure 1.23.
Single-threaded and non-collapsible heat exchangers are made of the tubes with a length of 3 ... 12 m, with a diameter of the inner tubes 25 ... 159 mm and external of 48 ... 219 mm, and nominal pressure for the outer pipes up to 6.4 MPa and for the internal up to 16 MPa. The collapsible structure of heat exchangers is provided by the strain compensation of the heat exchanger tubes. Figure 1.24 shows the structure of a collapsible multi-threaded heat exchanger of "annular tubes type structurally resembling shell and tube heat exchanger.
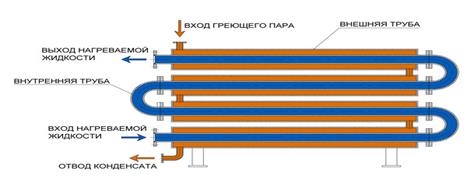
Figure 1.23 – The direction of coolants movement
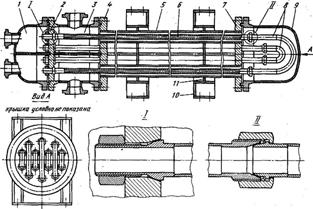
Figure 1.24 – Collapsible double-flow heat exchanger of «annular tubes type
The equipment consists of the shell tubes 5, which are expanded into the two tube sheets: average 4 and right 7. Heat exchanger tubes 6 are arranged inside of the shell tubes, one end of which is rigidly connected with the left tube sheet 2, and the other - can be moved. The free ends of the heat exchange tubes are connected in pairs bends 8 and closed by the chamber 9. The distribution chamber 1 has a role of the distribution of the coolant flow on the heat exchanger, and distribution chamber 3 has a role of the distribution of the coolant in the annulus. Shell tubes are rigidly connected with the backing 10 by the plate 11.
The advantages of the heat exchanger of "tube in tube" type are the ability to create a countercurrent regime, the establishment of the most appropriate speeds of the process of heat transfer, ease of manufacture, installation and maintenance, suitable for heating or cooling mediums under high pressure.
Temperature compensation is achieved by the deformation of the twin, which connects the inner tube and loosely placed in the cavity of the cover, uniting the ring space of the equipment.
The structure of the heat exchangers of «annular tubes» type allows to use as internal tubes the finned tubes. A method of finning is selected depending on the properties of the medium in the annular space of the heat exchanger.
The disadvantages of single-stream heat exchangers of the collapsible structure are the large number of flanges, which are the sources of leaks, non-compactness and labor repair, bulkiness, high cost due to the large consumption of metal on the outside of the tibe, not participating in the heat exchange, the complexity of cleaning the annular space.