
1.3 Air cooler exchanger
If the target process is not air heating, but the cooling of the hot air coolant, such equipments are called air cooler exchangers. Air cooler exchangers became more widely used. This is due to the much smaller value of the air as the coolant, compared with water.
Widespread in the industry got air coolers, in which air stream is used as a cooling agent, which is injected specially by installed fan. The usage of this type of equipments allows considerable saving of cooling water to reduce the amount of wastewater. It also eliminates the need to clean the exterior of the heat exchange tubes. Such equipments are used as condensers and coolers. The relatively low heat transfer coefficient from the air flow, which is characterised for these equipments, offset by significant finned outer of the surface of the tubes, as well as the relatively high-speed of air flow.
Classification of the air cooler exchangers.
Air cooler exchanger of different types are made to the appropriate standards, which provide a large range of largest surface, the degree and type of fin construction material, which is used for their manufacture (of various brands steel, brass, aluminum alloys, bimetal). Air cooler exchanger are classified by:
- a) the location of the tube bundles are divided into the following types:
- Horizontal;
- Zigzag;
- Small flow (for viscous and highly viscous);
- b) by purpose:
- Refrigerators;
- Compensators.
The main elements of the air cooler exchangers construction
Air coolers exchanger include the following main components and assemblies: the section of the finned heat exchanger tubes of various lengths (from 3 to 12 m), electric fans, diffusers and louvers to adjust air performance, load-bearing structures, in some cases, control mechanisms. Equipments are applicable for gas cooling and have advanced exterior surfaces, which characterized by the coefficient of the fins. Coefficients finned equipments have the range from 7.8 to 21. This is due to the fact that the heat flow from the gas tube to the material is significantly higher than that of the outer surface of the air.
The surface of the fins can be done in different ways: knurled or wound of edges, overmolded of plates, wire winding. Knurled edges are formed by extrusion of thick-walled billet between special rollers. The material in this case are relatively soft metals - copper, aluminum. Bimetallic tubes sometimes are used; in this case the inner tube material is selected depending on the operating conditions, the coolant, its thermal, physical and corrosion properties. It should be noticed that at this point of contact in the two tubes there is the additional thermal resistance, as shown by numerous studies, their thermal efficiency is reduced by 10-20% compared to monometallic tubes.
Wound finned tubes are made by winding mainly aluminum tape on the tubes and may be wrapped with a tape or interference in the pre-knurled groove depth of 0.5 mm and a tape carrier base metal tubes for greater rigidity and reduce thermal resistance.
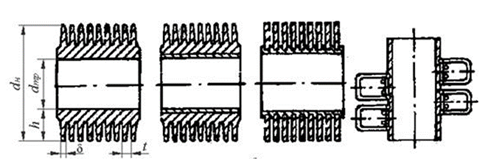
The plate fins are prepared by over molded plates of various configurations of the tubes by soldering or welding (in the main radiators of internal combustion engines). Figure 1.25 shows the different structures of finned tubes.
The mono tube of aluminum alloys are applied to a pressure of 1.6 MPa; carbon and stainless steel alloys – almost any possible pressure in the system. Finned tubes are collected into the bundles and may have from 2 to 8 rows of tubes. Tube bundles forming section, which are available with different numbers of turns on the tube space. The width of the sections of the various units is 1380 mm, and the height and length depend on the number of rows and the length of the tubes. They are available at pressure 0,6-6,4 MPa.
|
а)rolling monometallic |
b)rolling bimetallic |
c)wound in the groove |
d) loopy-wire |
|
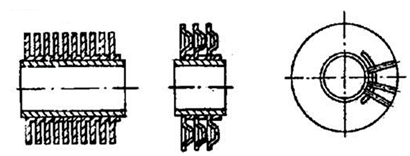
e) pressed-on and plate |
f) wound with an L-shaped strip |
Figure 1.25 – The types of finned tubes of air coolers exchanger
Figure 1.26 shows a horizontal type of equipment, where the finned heat exchanger tubes bundles are arranged horizontally, and Figure 1.27 shows equipments, where the tube bundles are arranged in a zigzag manner and tent.
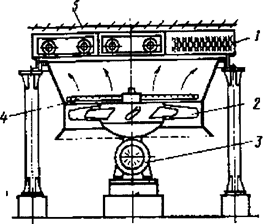
1 – finned tubes section; 2 – fan wheel; 3 – electric motor; 4 – manifold of the injection of the purified water; 5 – louvers
Figure 1.26 – Scheme of the horizontal air coolers exchanger.
Для повышения эффективности аппарата в его конструкции предусмотрен коллектор впрыски очищенной воды 4, автоматически включающийся при повышенной температуре окружающей среды в летний период работы. При низких температурах (зимой) можно отключать электродвигатель и вентилятор; при этом конденсация и охлаждение происходят естественной конвекцией.
|
а) roofed |
b) zigzag |
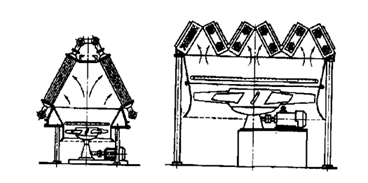
Figure 1.27 – Schemes of air cooler exchangers
Accommodation of the bundles of finned tubes in the form of a tent and a zigzag allows to have a large heat exchange surface at the same occupied area.
To improve the efficiency of the equipments, their structure includes an injection of treated water 4, which is automatically activated at elevated ambient temperature during the summer period of work. At low temperatures (in winter), it is possible to turn off the motor and a fan; condensation and cooling occur by natural convection.
In addition, the intensity of heat removal can be controlled by varying the flow of air pumped by changing of the fan blade pitch angle. For this purpose air cooling exchangers are provided with a mechanism to remotely turn the blades manually or pneumatically and shutters, which are installed over the heat exchange section. Louvered flaps can be rotated manually or automatically by an actuator.
The heat exchange section of air cooler exchanger consists of four, six or eight rows of tubes 3 (Figure 1.28), which are arranged at the vertices of equilateral triangles in two tube sheets 1. Tubes are fastened by flare or flare with welding. Section 4 is reinforced by metal frame to ensure rigidity of the tube bundle. However, the operation of the nuts on the studs 2, connecting the sheet to the frame, must be unscrewed a distance greater than the possible temperature extension tubes. In the tube bundle each tube can has an individual deflection. To avoid the contact of the ribs of the top row of tubes with the ribs of tubs of the bottom row of tubes between adjacent rows at several locations along the tube, which are placed spacers 15 with width of 5 mm, which are made from the aluminum tape with a thickness of 2 mm.
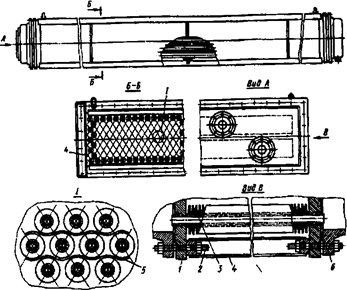
Figure 1.28 – The heat exchange section of the air cooler exchanger
The cover 6 are fixed to the tube plates of heat exchange sections permanently at high pressure or high heels. If the section of equipment is multipass, the covers are provided with partitions, which are divided the bundles. Removable covers are usually made of cast steel. As indicated, the air cooler exchangers have fins on the outer surface because the heat transfer coefficient on the outside surface of tubes is about an order lower than the coefficient for the inner surface. The air cooler exchangers use the fans with a diameter of wheels of up to 7 m. Fan wheels are manufactured by welded aluminum or fiberglass, which are made of sheet steel with thick of 2 mm. Drive motors can be single or dual speed. When using two-speed motors with decreasing ambient temperature, it is possible to operate at a lower fan speed.
Advantages:
1) The ability to work with complex (in terms of heat transfer) heat coolants - air and high-viscosity fluids;
2) The large surface of the heat transfer from the complex (in terms of heat transfer) coolant under high compactness of heat exchanger;
3) The possibility of using air as the coolant, which is economically advantageous because it allows to save more expensive recycled water than air.
Disadvantages:
1) The fin-plate requires for manufacturing the high thermal conductive material (steel is not always suitable, but aluminum or copper is often used);
2) Air cooler exchanger is still much more cumbersome than the heat exchangers which are intended for cooling water.