
1.6 Coil heat exchangers
Coil heat exchangers - is apparatus in which the heat exchange surface is a flat or a volume coil arranged in the heat exchanger housing and high pressure coolant is fed to the tube space of the coil. These devices are used in the chemical, petrochemical, gas and in refrigeration and food industries. Heat exchangers of this type is defined as a non-rigid structure devices with compensation of thermal stresses as a result of free elongation of the coil.
Classification coils of heat exchangers.
These devices are classified according to destination, the state of aggregation and coolant circuit of their relative motion, configuration heat exchanger elements and their orientation, according to their location and the type of layout, the nature of the thermal contact.
As technological purpose - this exchanger recuperative heat exchangers.
By coil configuration:
- Flat spiral (Figure 1.35, a);
- Zigzag (Figure 1.35, b);
- Three-dimensional cylindrical shape (figure 1.35, c);
- Conical shape (Figure 1.35, d).
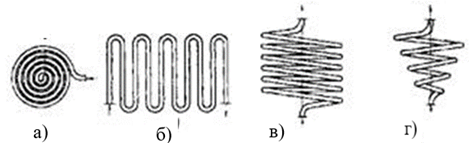
Figure 1.35 – Heat exchange element coils of heat exchangers
By targeting the heat exchange elements in the space:
- With horizontal coils;
- With vertical coils;
- With inclined coil.
On location the heat exchanger elements:
- With internal coils mounted within the housing;
- External coils placed on the housing.
Typically, devices with internal heat exchange elements are called submersible and external - heat exchangers with the outer coils.By the number of taps of the coil one and multiple (multi-element).
By the nature of the thermal contact with the coolant heat exchanger elements:
- Submersible;
- Irrigation.
Construction coils of heat exchangers.
The design of the heat exchanger coil is shown in Figure 1.36. The device has a housing 1 in which is placed a coil 3 or the system of coils. The turns of the coil are oriented along a helical path. When a large heat exchange surface area along the length of coils are drawn from several sections. To avoid sagging of pipes with a large number of turns and the large diameter of each coil winding is fixed by bolts on the racks.
The difference in the heat exchanger coolant pressure may reach up to 10 MPa.
In the multiple-coil apparatus twisted tube ends are welded into tube sheets. The heat transfer surface consists of a plurality of coils disposed along a helix in the annular space between the inner drum and the housing. One of the coolant moves inside the coil tubes.
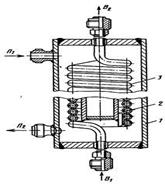
Figure 1.36 – Singleton coiled heat exchanger industrial value