
2.6 Radiation furnaces
Radiation heating furnaces are used for heating substances to low temperatures (up to about 300 °C), with a small amount of them, and if it is necessary using cheap low value fuels in cases where special importance is attached to low costs for the furnace construction.
In radiation furnace all tubes through the substance to be heated placed on the combustion chamber walls. Therefore, the radiation furnace combustion chamber significantly larger than that of the convection.
All tubes directly subjected to the gaseous medium, which has a high temperature. This is achieved by:
- Reduction of the total heat transfer area of the furnace, since the amount of heat given unit area of the pipe, by radiation at the same temperature (especially at high temperatures of the medium) is considerably larger than the amount of heat that can be transferred by convection;
- Good preservation for lining of tube coils because its temperature is reduced, firstly, by the direct part of its closing pipes, secondly, due to the impact of heat radiation cooler lining pipes.
Typically impractical to cover all walls and ceilings of the pipes, as it is limited by heat radiation exposed surfaces, and as a result reduced the total amount of heat given unit area of the pipe. For example, modern types of furnaces vat ratio of the effective open surface of the total inner surface of the furnace in the range of 0.2-0.5. Clean the oven radiation because of the simplicity of design and high thermal load of pipes have the lowest capital cost per unit of heat transferred.
However, they do not allow to use the heat of the combustion products, as is the y radiation-convection oven. Therefore, radiation furnaces operate with a lower thermal efficiency.
Schematic diagrams of the radiation type furnaces are shown in Figure 3.81. The total lack of these furnaces - low efficiency due to the absence of convection tube bundle, leading to large losses of heat from the flue gas (high temperature of flue gases leaving the oven). Several higher efficiency in furnaces of this type is obtained by heating the products to low temperatures and low calorific heating surface tubes or heat recovery of flue gases after the furnace.
Furnaces with a vertical pipe arrangement (Figure 2.41, b) are adapted to operate on gaseous fuels. They require less change tube as the tube are pulled up using electro-grapnels, area than other types of furnaces. These furnaces are not required to set areas for the top of the chimney. The ceiling of the furnace shown in Figure 2.41 (a), the metal cone 3 is installed that transmits heat radiation upper portions of pipes, which intensifies the heat transfer by radiation and increases the degree of uniformity of heating pipes along the length.
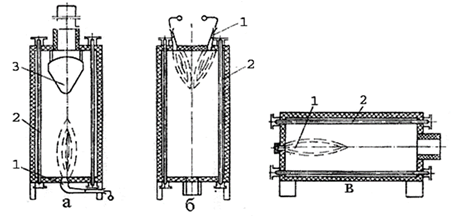
1 – nozzle; 2 – pipe coil; 3 – the heat radiating metal cone
Figure 2.41 – Tubular furnace radiation type (longitudinal cuts).
The parallel arrangement of the axes of nozzles and pipes in the absence of heat radiating cone (figure 3.81, b) results in a significant uneven heating along the length of the tubes. The advantage of the furnace (Figure 2.41, b) to (2.41, a) – is the ability to heat recovery of flue gases.
The advantage of radiant oven with horizontal pipes (Figure 2.41, c) it is the ability to easily and affordably maintain its installation and repair.